Publications
- Orcid ID: 0000-0003-2192-4416
- ResearcherID: A-9752-2009
- Google Scholar: 8kg1qzsAAAAJ
- HAL (open archive): dralucas
in review
-
Landslide-Tsurrogate v1.0: A computationally efficient framework for probabilistic tsunami hazard assessment applied to Mayotte (France)GMD, in review.
-
Frictional weakening in the highly mobile 2025 Blatten rock–ice avalancheNat. Geosc., in review.
-
Bayesian Hapke inversion of (4) Vesta’s avalanches and ejecta: photometric constraints on regolith evolutionA&A, in review.
-
Seismically Triggered Recent Boulder Falls After S0235b Marsquake on Cerberus Fossae, MarsIcarus, in review.
-
Investigating the Detectability of Body Wave Phases from Tidal Ice Cracking Events on Titan with the Dragonfly Short-Period SeismometerJGR-Planets, in review.
2025
2024
-
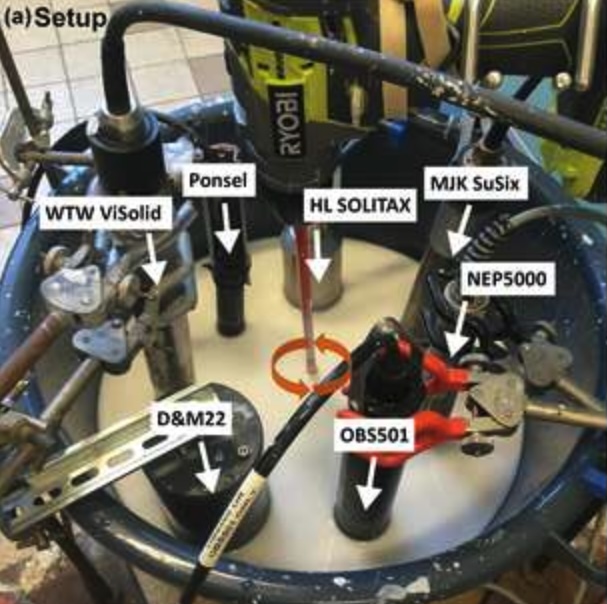 Intercomparison of optical scattering turbidity sensors for a wide range of suspended sediment types and concentrationsCATENA, 2024.
Intercomparison of optical scattering turbidity sensors for a wide range of suspended sediment types and concentrationsCATENA, 2024.
2023
-
Uncovering a 70-year-old permafrost degradation induced disaster in the Arctic, the 1952 Niiortuut landslide-tsunami in central West GreenlandScience of The Total Environment, 2023.
-
Permafrost molards as an analogue for ejecta-ice interactions at Hale Crater, MarsIcarus, 2023.
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
-
First quantification of relationship between dune orientation and sediment availability, Olympia Undae, MarsEarth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018.
2017
-
Thermally anomalous features in the subsurface of Enceladus’s south polar terrainNature Astronomy, 2017.
2016
-
-
Compositional and spatial variations in Titan dune and interdune regions from Cassini VIMS and RADARIcarus, 2016.
2015
-
-
Stratigraphy of Aeolis Dorsa, Mars: Stratigraphic context of the great river depositsIcarus, 2015.
-
-
Resolving the era of river-forming climates on Mars using stratigraphic logs of river-deposit dimensionsEarth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015.
-
2014
-
Global mapping and characterization of Titan’s dune fields with Cassini: Correlation between RADAR and VIMS observationsIcarus, 2014.
-
-
Low palaeopressure of the martian atmosphere estimated from the size distribution of ancient cratersNature Geoscience, 2014.
-
A radar map of Titan Seas: Tidal dissipation and ocean mixing through the throat of KrakenIcarus, 2014.
2013
-
-
Pacing early Mars river activity: Embedded craters in the Aeolis Dorsa region imply river activity spanned ≳(1–20)MyrIcarus, 2013.
2012
-
Morphological and mechanical characterization of gullies in a periglacial environment: The case of the Russell crater dune (Mars)Planetary and Space Science, 2012.
-
2011
-
Stratigraphy, mineralogy, and origin of layered deposits inside Terby crater, MarsIcarus, 2011.
-
On the run-out distance of geophysical gravitational flows: Insight from fluidized granular collapse experimentsEarth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011.
2010
2009
-
New insight on genetic links between outflows and chasmata on Valles Marineris plateau, MarsGéomorphologie: relief, processus, environnement, 2009.
2007
Other publications
-
Geomorphic transport from historical shape from motion: Implications for tropical and alpine environmentsESSOAr Preprint, 2019.
-
FARMYARD: A Generic GPU-based Pipeline for Feature Discovery from Massive Planetary LiDAR DataTechRxiv Preprint, 2022.
-
POPS: An Efficient Framework for GPU-based Feature Extraction of Massive Gridded Planetary LiDAR DataHAL Preprint, 2022.
-
Titan’s surface geologyIn Titan: Interior, Surface, Atmosphere, and Space Environment, 2014.
Thesis
-
Geomorphic transports in Terrestrial & Planetary Critical Zones
Lucas, Antoine
HDR (Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches), Université Paris Cité, 2025.Abstract
The granular materials—whether they descend slopes as avalanches of debris or rock, or are shaped by wind into vast sand seas—dominate many solid bodies within the Solar System. These processes that shape planetary surfaces serve as witnesses to forcing mechanisms. The study presented condenses a decade of research on sediment mobility, conducted quantitatively and integrated with: (i) physical or phenomenological models along with numerical simulations of sediment transport; (ii) multi-wavelength remote sensing measurements supported by radiative modeling and photogrammetry. Applied to the dune fields of Titan, Mars, and Earth’s deserts, these approaches demonstrate how aeolian conditions, sediment supply, and substrate texture (whether rocky or icy) influence the orientation and wavelength of dunes. They also quantify transitions between dust and sand that feed into planetary atmospheric cycles. This framework offers a new perspective on slope instability phenomena such as landslides and debris avalanches. Analyzing the morphodynamic system through the Solar System reveals a common phenomenological framework, allowing observations, measurements, seismic recordings, and numerical modeling to be reconciled. Finally, this approach retraces the mechanics of propagation and upstream-downstream coupling between slope instabilities (e.g., landslides, debris avalanches) and fluvial responses. This work leads to numerous methodological and thematic insights. Notably, it seeks a better understanding of how changes in climatic conditions affect sediment transport over different time scales. For example, if it is demonstrated that permafrost degradation increases instability occurrences, the study also explores whether these instabilities’ behavior is similarly impacted. This has implications for sediment availability, unaltered material availability, and carbon fluxes on Earth. By linking granular physical processes with remote sensing and comparative planetary science, this work provides a coherent framework to interpret—and ultimately predict—geomorphological traces of climate change on Earth.
-
Dynamique des instabilités gravitaires par modélisation et télédétection: Applications aux exemples martiens
Lucas, Antoine
PhD Thesis, IPGP, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (IPGP), 2010.Abstract
EN: Slope instabilities take part in weathering and transport processes at the surface. The runout distance is extensively used in analysis of landslide dynamics and in the calibration of the rheological parameters involved in numerical modelling. However, the unknown impact of the uncertainty in the shape of the initial released mass on the runout distance and on the overall shape of the deposit questions the relevance of these approaches. Indeed, the shape of the initial scar is generally unknown in real cases. Our study is based on numerical simulations coupled with remote sensing data analysis. The model used in this study has been intensively compared with laboratory experiments and well constrained natural cases in order to establish its range of use. We have also developed a pre-event topographic reconstruction method using remote sensing data allowing the study of the topographic and initial failure plane geometry effects. We show that the runout distance is a robust parameter that is only poorly affected by the initial scar geometry. On the contrary, the extent of the deposits perpendicular to the main mass displacement direction is shown to be controlled by the scar geometry, providing a unique tool to retrieve information of the initial failure geometry, as well as on the released volume. A feedback analysis of Martian landslides shows excellent agreement between numerical results and geomorphological evidence, providing insight into the initial landsliding conditions. In addition, we introduce a new empirical dissipation parameter allowing a good prediction of the runout in the simulation without any calibration for a given geological context.
FR: Les instabilités gravitaires contribuent aux processus de transport de matière à la surface des planètes et constituent des risques importants pour les populations sur Terre. Afin d’apporter des contraintes sur la dynamique des instabilités gravitaires, notre étude se base sur le couplage entre simulation numérique et analyse des données par télédétection. Le modèle utilisé s’est montré capable de reproduire des observations en laboratoire ainsi que la dynamique enregistrée par des signaux sismiques pour un exemple terrestre. En outre, nous avons développé une méthode de reconstruction topographique pré-glissement en utilisant les données satellitaires afin d’étudier les effets des conditions initiales. En effet, la distance d’arrêt (runout) des dépôts est très largement utilisée dans l’analyse de la dynamique des glissements de terrain ainsi que dans la calibration des paramètres rhéologiques impliqués dans la modélisation, et ce malgré les incertitudes sur la géométrie initiale. Nous montrons par des tests théoriques que le runout est faiblement affecté par la géométrie du plan de rupture. Au contraire, l’extension latérale se révèle être contrôlée par la géométrie initiale ce qui fourni un cadre unique pour remonter également au volume initial. L’application aux exemples martiens apporte des contraintes sur les conditions de mise en place et ouvre de nouvelles perspectives pour la compréhension de la dynamique de ces processus. En outre, nous introduisons un nouveau paramètre de dissipation empirique indépendant de la topographie permettant, sans calibration, de retrouver par la simulation la bonne distance de runout dans un contexte géologique donné.